Assalamualaikum...
waaa.... i think its been quite long i have not posting anything :0..This is because the class keep being postponed so, i have nothing to write :(
oK lets proceed to our main topic. So the topic for this week is....
oK lets proceed to our main topic. So the topic for this week is....
CABLING
What is network cabling?
Cable is the medium through which information
usually moves. In some cases, a network will utilize only one type of cable,
other networks will use a variety of cable types. The type of cable chosen for
a network is related to the network's topology, protocol, and size.
Type of cable
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable
- Coaxial Cable
- Fiber Optic Cable
- Wireless LANs
Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable (UTP)
>> has four pairs of wires inside the jacket.
>> Each pair is twisted with a different number of twists per inch to help eliminate interference from adjacent pairs and other electrical devices.
>>The tighter the twisting, the higher the supported transmission rate and the greater the cost per foot.
>> Each pair is twisted with a different number of twists per inch to help eliminate interference from adjacent pairs and other electrical devices.
>>The tighter the twisting, the higher the supported transmission rate and the greater the cost per foot.
>>Disadvantage: may be susceptible to radio & electrical frequency interference.
 | |||
| Unshielded twisted pair |
Types of UTP
Category
|
Speed
|
Use
|
1
|
1 Mbps
|
Voice Only (Telephone Wire)
|
2
|
4 Mbps
|
LocalTalk & Telephone
(Rarely used)
|
3
|
16 Mbps
|
10BaseT Ethernet
|
4
|
20 Mbps
|
Token Ring (Rarely used)
|
5
|
100 Mbps (2 pair)
1000 Mbps (4 pair)
|
100BaseT Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet
|
5e
|
1,000 Mbps
|
Gigabit Ethernet
|
6
|
10,000 Mbps
|
Gigabit Ethernet
|
UTP Connector
>>The standard connector for UTP = RJ-45
connector.
>> plastic connector that looks like a large telephone-style connector.
>>A slot allows the RJ-45 to be inserted only one way.This standard designates which wire goes with each pin inside the connector.
>> plastic connector that looks like a large telephone-style connector.
>>A slot allows the RJ-45 to be inserted only one way.This standard designates which wire goes with each pin inside the connector.
 |
| RJ-45 Connector |
Shielded Twisted Pair Cable (STP)
>>consist of 2 individual wires.
>>suitable in environments with lots of potential
interference or in extremely sensitive environments that may be susceptible to
the electrical current in the UTP.
>>Shielded cables can also help to extend the
maximum distance of the cables.
>>Shielded twisted pair cable is available in three
different configurations:
- Each pair of wires is individually shielded with foil.
- There is a foil or braid shield inside the jacket covering all wires (as a group).
- There is a shield around each individual pair, as well as around the entire group of wires (referred to as double shield twisted pair).
>>has a
single copper conductor at its center.
>>A plastic layer provides insulation
between the center conductor and a braided metal shield.
>>The metal
shield helps to block any outside interference from fluorescent lights, motors,
and other computers.
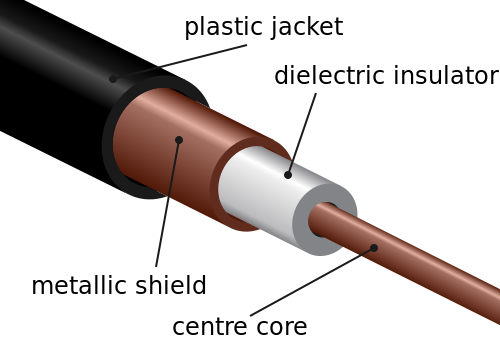 | |
| coaxial cable |
Coaxial Cable Connector
>>most common type of connector= Bayone-Neill-Concelman (BNC) connector.
>>Different types of adapters are available for BNC connectors:
Fibre Optic Cable
>> consists of a center glass core surrounded by several layers of protective materials.
>>transmits light rather than electronic signals eliminating the problem of electrical interference.
>>ideal for certain environments that contain a large amount of electrical interference.
>>the standard for connecting networks between buildings, due to its immunity to the effects of moisture and lighting.
>>transmit signals over much longer distances than coaxial and twisted pair.
>>carry information at vastly greater speeds.
>>more difficult to install and modify.
*single mode *Multimode
provide more distance larger diameter
>>Different types of adapters are available for BNC connectors:
- T-connector
- barrel connector
- terminator.
 | |
| a BNC Connector |
Fibre Optic Cable
>> consists of a center glass core surrounded by several layers of protective materials.
>>transmits light rather than electronic signals eliminating the problem of electrical interference.
>>ideal for certain environments that contain a large amount of electrical interference.
>>the standard for connecting networks between buildings, due to its immunity to the effects of moisture and lighting.
>>transmit signals over much longer distances than coaxial and twisted pair.
>>carry information at vastly greater speeds.
>>more difficult to install and modify.
two
common types of fiber cables
*single mode *Multimode
provide more distance larger diameter
more expensive
#both cables provide high bandwidth at high speeds.
#both cables provide high bandwidth at high speeds.
 | |||
| fibre optic cable |
summary of ethernet cabling
Specification
|
Cable Type
|
10BaseT
|
Unshielded
Twisted Pair
|
10Base2
|
Thin
Coaxial
|
10Base5
|
Thick
Coaxial
|
100BaseT
|
Unshielded
Twisted Pair
|
100BaseFX
|
Fiber
Optic
|
100BaseBX
|
Single
mode Fiber
|
100BaseSX
|
Multimode
Fiber
|
1000BaseT
|
Unshielded
Twisted Pair
|
1000BaseFX
|
Fiber
Optic
|
1000BaseBX
|
Single
mode Fiber
|
1000BaseSX
|
Multimode
Fiber
|
Wireless LANs
>> use high frequency radio signals, infrared light beams, or lasers to communicate between the workstations, servers, or hubs.
>> Each workstation and file server has some sort of transceiver/antenna to send and receive the data.
>> For longer distance, wireless communications can also take place through
cellular telephone technology, microwave transmission, or by satellite.
fuhhh..tired already






